|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready... |
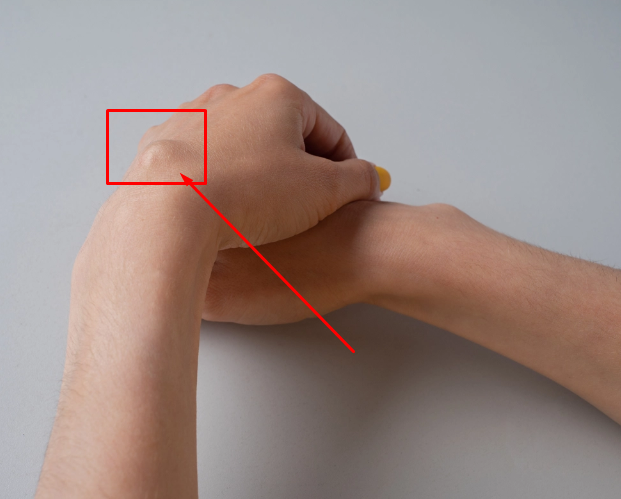
Lipoma
Lipoma is a benign tumor made up of fatty tissue. Learn about the symptoms and treatment options for various types of lipomas.
A lipoma is a benign tumor composed of fatty tissue. Among soft tissue tumors, lipomas are the most common type. They feel soft to the touch, can usually be moved, and are generally painless. Many lipomas are small, typically less than one centimeter in diameter, but some can grow larger than six centimeters. Lipomas are more commonly found in people aged 40 to 60, although children can also develop them. Some believe that lipomas can transform into cancer.
Types of Lipoma:
There are various types of lipomas, including:
- Angiolipoma: A painful lump under the skin. It shares characteristics with other lipomas.
- Angio Lipo Leiomyoma: An acquired lipoma. A single, asymptomatic lump under the skin. Upon examination, it contains soft muscle cells, blood vessels, connective tissue, and fat.
- Neural Fibrolipoma: Excessive growth of fibro-fatty tissue along the nerve trunk, causing pressure on the nerves.
- Chondroid Lipoma: Found deep in the leg of women. It is a hard, yellow tumor.
- Spindle Cell Lipoma: Asymptomatic. Found under the skin of the back, neck, and shoulders in older men. It grows slowly.
- Pleomorphic Lipoma: Similar to spindle cell lipoma, these are mostly found on the backs and necks of older men.
- Intradermal Spindle Cell Lipoma: Typically affects women and occurs on the head, neck, abdomen, chest, back, arms, and legs.
- Hibernoma: Contains brown fat. The most common type of lipoma is ‘superficial subcutaneous lipoma,’ which is located just below the skin. These are commonly found on the chest, back, abdomen, thighs, and arms.
Treatment:
Treatment for lipomas is generally not necessary unless they cause pain or hinder movement. They can be removed for cosmetic reasons. If a lipoma is large or suspected to be malignant, it can be surgically removed and examined histopathologically. These lipomas are usually removed through simple surgery. In 1-2% of cases, a lipoma may recur after surgery.
Keywords: lipoma, tumor, symptoms, treatment, fatty tissue, angiolipoma, spindle cell lipoma
Writer: Vice Principal and Associate Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, Dhaka National Medical College and Hospital.